One of the trendiest buzzwords in business today is cloud computing. It has changed how businesses communicate, manage computer resources, and store, access, and share information.
With the introduction of the internet, cloud computing has opened up new avenues for business by enabling organizations to go beyond the limitations of traditional on-premises IT infrastructure.
Modern organizations may benefit from the flexibility, efficiency, scalability, security, enhanced collaboration, and lower costs that cloud computing provides.
Although the COVID-19 epidemic has hastened cloud adoption, it is expected to continue in 2022, particularly if hybrid work becomes a central role.
Therefore, in order to fully benefit from cloud-powered solutions, it is essential to grasp the fundamentals of cloud computing, regardless of whether a business now employs cloud services or plans to do so in the next year.
This blog will discuss the specifics of cloud computing, how it works, its pros and pitfalls, and how businesses may better safeguard their SaaS data.
Before going into the deep, let’s see what is cloud computing.
What is cloud computing?
The distribution of on-demand computing services, including apps, storage, and processing power, often through the internet and on a pay-as-you-go basis, is described as “cloud computing” by ZDNet.
The cloud is just a slang phrase for the internet. Organizations are said to be functioning in the cloud when they store data in virtual data centers or access applications through the internet rather than depending on the hard drive in their device or on-premises IT infrastructure.
Simple examples of cloud computing include “servers in a third-party data center” and entirely serverless applications that are geo-redundant and endlessly scalable. Expandable and dynamic cloud servers and services are currently available.
How is cloud computing implemented?
When computer resources like IT infrastructure or data centers are delivered via the internet, this is referred to as cloud computing.
Instead of creating and maintaining their own IT infrastructure or data center, this strategy enables organizations to rent storage space or access software packages from a cloud service provider.
Companies just pay for the resources they use when adopting cloud computing services, which is a significant advantage.
The procedures involved in cloud computing may be separated into frontend and backend to help in understanding its technological components.
Users may use a cloud computing application or an internet browser to access data and programs that are stored in the cloud thanks to the frontend component. Servers, computers, and databases make up the backend, which houses the data storage.
History of cloud computing
The term “cloud computing” was first used in a 1996 Compaq internal paper, claims Technology Review.
When Salesforce became the first business to provide corporate software via the internet, the year 1999 marked a turning point for cloud computing. Additionally, this marked the launch of software as a service (SaaS).
Another important advancement in cloud computing came with the debut of Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2002. Its collection of cloud-based services encompassed human intelligence, processing, and even storage.
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), which Amazon introduced in 2006, enables both consumers and organizations to rent virtual machines and run their own computer programs.
The launch of browser-based workplace apps by Google Workspace (now Google Workspace) in 2009 marked yet another significant turning point in the history of cloud computing.
Microsoft launched Microsoft Azure in the same year, and shortly after, businesses like Oracle and HP did likewise.
Examples of cloud computing
Virtual computers, databases, and full serverless applications are all part of the cloud. Cloud computing includes the following examples:
1. Salesforce: Salesforce.com is a SaaS company that focuses in managing client relationships (CRM). Users may work from anywhere thanks to the company’s corporate tools, which assist coordinate marketing, sales, customer service, etc.
2. DigitalOcean: IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) provider for software developers, DigitalOcean is situated in New York. DigitalOcean is used by businesses to scale and deploy applications that operate concurrently across several cloud servers.
3. Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure is a great illustration of a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that covers the whole application development lifecycle, from development through deployment and beyond. Developers have access to a wide variety of tools, languages, and frameworks via Azure.
4. Dropbox: Dropbox is a cloud-based file storage service that lets users sync files to their devices and keep them there so they can access them from anywhere.
Additionally, it enables users to collaborate successfully by enabling the online sharing of huge assets, including pictures and movies.
What role does cloud computing play?
Before the advent of the cloud, businesses had to download software or apps onto their physical PCs or on-premises servers in order to utilize them.
Building and operating one’s own data centers or IT infrastructure is very difficult for any firm. Allocating a big number of IT administrators and resources is difficult, even for those who operate their own data centers.
In the history of the technology sector, the advent of cloud computing and virtualization represented a paradigm change.
Cloud computing enables organizations to rent computing resources from cloud service providers rather than building and operating their own IT infrastructure and paying for servers, electricity, real estate, etc.
By doing this, organizations may avoid the high upfront expenses and challenging management of owning their own data centers.
By renting cloud services, businesses only pay for the processing power and disk space they really utilize. This makes it possible for businesses to predict expenses more precisely.
Businesses save a ton of time, effort, and money since cloud service providers handle the labor-intensive management and maintenance of the IT infrastructure. Additionally, the cloud enables businesses to effortlessly expand or contract their computer infrastructure as required.
The cloud, as opposed to the conventional on-premises data center architecture, provides simple access to data from anywhere and on any internet-connected device, facilitating efficient collaboration and increasing productivity.
What applications of cloud computing are most typical?
Every company utilizes the cloud to access digital services to optimize processes, increase communication, productivity, service delivery, and more.
This includes startups, huge enterprises, and government organizations. Some of the most popular applications for cloud computing are listed below.
1. Storage: File storage is one of the most popular applications for cloud computing. While there are many ways to store and access data, including USB drives, external hard drives, and PC hard drives, cloud storage allows organizations to easily access data from anywhere on any device with an internet connection.
Cloud storage solutions like Amazon S3, DropBox, or OneDrive provide safe data access while also enabling organizations to increase or decrease storage capacity in accordance with their needs.
2. Database: Another common corporate use case is cloud databases. “A database service produced and accessible via a cloud platform,” according to IBM, is what a cloud database is.
Most of the same features of a conventional database are also provided by a cloud database, but it also has extra advantages including flexibility, cost savings, failover support, specialist knowledge, and more.
3. Web applications: Web apps are a necessary tool for enterprises in the modern day. With the use of cloud technology, anybody with a web browser may use web-based applications to instantly access information from a distance.
This enables business people to connect with clients, provide them the information they need while they’re on the road, and collaborate with coworkers from any location.
4. Collaboration: Cloud-based platforms, like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, have emerged as the clear option for organizations wishing to interact both internally between departments and externally with customers due to their simple accessibility, integration, flexibility, and simplicity of use.
Teams, Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Word, Google Docs, Gmail, and other effective business technologies are designed to increase productivity and teamwork.
5. SaaS applications: Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) systems, like Salesforce, enable companies to effectively manage customers, automate marketing, and store, organize, and retain data. SaaS solutions provide a high degree of functionality and don’t need hardware or software administration.
What are the main types of cloud computing?
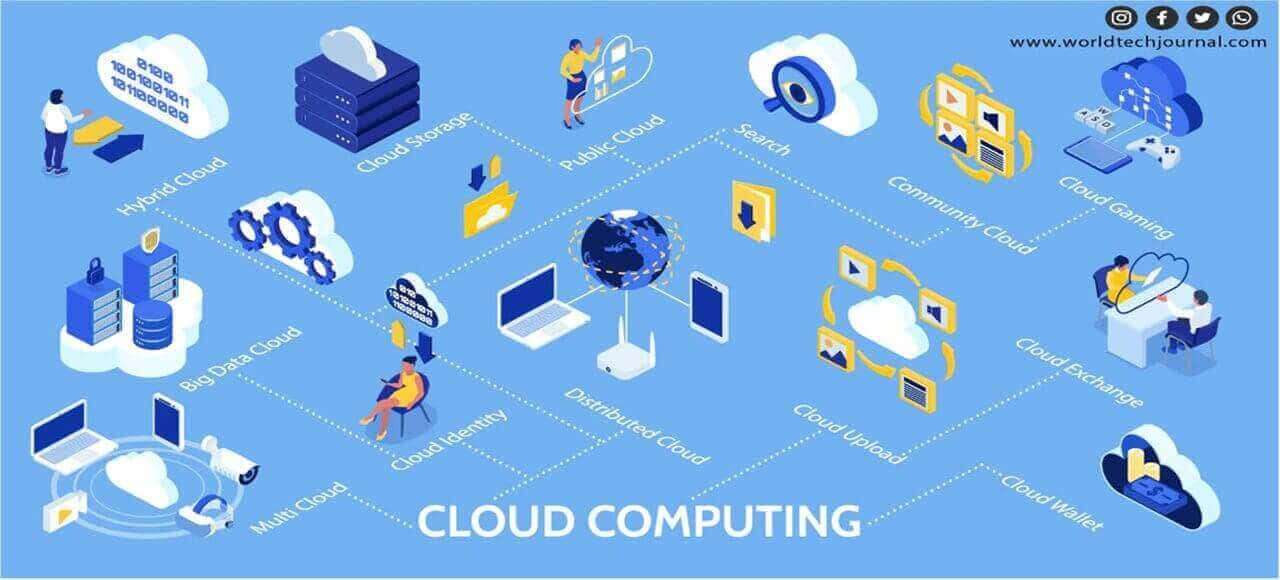
Public, private, hybrid, and multicloud cloud computing is the four primary subtypes.
1. Public cloud
“An IT paradigm where on-demand computing resources and infrastructure are managed by a third-party provider and shared with many enterprises over the public internet,” according to VMware.
Cloud service providers provide a range of services to people and organizations that rent these services on a monthly or pay-per-use basis, including Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and SaaS.
The top five cloud providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and IBM Cloud.
2. Private cloud
Unlike a public cloud where computing resources are shared among many tenants, a private cloud or internal cloud is where the IT infrastructure (hardware and software resources) is exclusively committed to a single enterprise.
For enterprises where upholding regulatory regulations, security, and control are top priorities, a private cloud environment is appropriate.
A private cloud is often hosted in a company’s data center and utilizes that company’s hardware. To a third-party supplier that remotely maintains the computer resources, a company may outsource hosting.
3. Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud is made up of both public and private cloud infrastructures. This approach is used by businesses to increase their computing capability. Businesses may use the public cloud to expand the capabilities of a private cloud after it has reached its maximum capacity.
Businesses may adjust their computing capacity in a hybrid cloud based on traffic or service needs. Businesses may save money, time, and effort by not having to buy and manage new servers as a result.
4. Multicloud
Utilizing two or more public or private clouds, or a mix of both, from different cloud providers is known as multicloud.
A multicloud strategy enables organizations to choose the finest services from many cloud suppliers in accordance with their financial and technological constraints, geographical needs, and other factors. With the help of this paradigm, enterprises may use many clouds for various needs.
For instance, a company may utilize one cloud for testing and developing software, another for disaster recovery and data backup, and still another for data analytics.
Main 3 categories of cloud computing services?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service are the three categories of cloud computing services (SaaS).
1. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IaaS is a kind of cloud computing service where cloud providers use the internet to offer and administer virtualized computer equipment.
Businesses may get necessary resources, such as operating systems, networking, storage space, development tools, etc., on demand rather than building their own internal IT infrastructure. This reduces the need for IT employees and lowers hardware and software expenses.
2. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Since cloud providers do the heavy lifting, PaaS enables organizations to focus on the creation, implementation, and maintenance of software applications and services without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure.
Developers and programmers have access to the platform and solution stack for applications and software as well as IT infrastructure with PaaS. AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure are a few PaaS examples.
3. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS) offers organizations ready-to-use applications that are provided to users online. SaaS companies handle all of the underlying infrastructures, including hardware, software, data storage, patch management, and hardware/software upgrades.
Businesses must subscribe to the services they wish to utilize in order to use SaaS, which is a subscription-based approach. SaaS programs may be accessed immediately via web browsers, thus there’s no need to download or install them.
With an active internet connection, SaaS enables consumers to access web-based applications from any location and at any time. Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Microsoft 365 are a few well-known SaaS products.
Advantages of cloud computing
Businesses may function more effectively and from nearly any location thanks to cloud computing. Among the advantages of cloud computing are:
1. Cost savings: Saving money is one of the biggest advantages of cloud computing. Businesses may drastically cut their capital expenditures since they no longer need to invest in IT infrastructure or hardware purchases.
2. Scalability and flexibility: Cloud computing gives companies of all sizes more freedom. They can easily scale up or down computer resources according on their demands and budget, whether they need more bandwidth, processing power, or storage space.
3. Security: Today’s corporations are very concerned about data security. To guarantee that sensitive data in the cloud is handled and kept in a safe manner, cloud suppliers offer cutting-edge security features like authentication, access management, data encryption, etc.
4. Mobility: Using the internet and cloud computing, users may access company data at any time and from any location using any device. With information readily accessible, workers may continue to be productive while on the road.
5. Increased collaboration: Cloud apps make it easy and hassle-free for organizations to collaborate by enabling safe information access and sharing as well as seamless communication. With the use of cloud computing, several users may transparently and concurrently edit papers or work on data.
6. Disaster recovery: Any size firm may suffer irreversible harm from data loss and downtime.
To provide high application availability and business continuity, major cloud suppliers are well-prepared to endure unanticipated disruptive events including hardware/software failure, natural catastrophes, and power outages.
7. Automatic updates: Manually updating all of the organization’s software might consume a significant amount of IT staff time. With cloud computing, however, service providers continuously update systems with the most recent technology to provide organizations access to the most recent software versions, servers, and processing capacity.
Disadvantages of cloud computing
Operating on the cloud has a ton of benefits. Before opting to make the switch to the cloud, businesses should be aware of a few drawbacks. The top five drawbacks of cloud computing are listed below.
1. Downtime: Due to the fact that cloud computing systems are totally dependent on the internet, companies are unable to access the data or apps stored in the cloud when there is no active internet connection. In 2020, Google had three significant outages that had a negative impact on the majority of its services and users throughout the world.
2. Vendor lock-in: A fundamental problem in cloud computing is moving a company’s workloads and services from one cloud provider to another. Compatibility or integration problems may arise as a result of differences across cloud infrastructures. Inappropriate transition management might expose an organization’s data to unwanted security flaws.
3. Limited control: Organizations adopting cloud computing services have little control over their data, apps, and services since the cloud infrastructure is entirely owned and maintained by the cloud provider.
Because of this, it’s critical to have a valid end-user licensing agreement (EULA) in place so that businesses are aware of their rights and obligations while using cloud infrastructure.
4. Security: Security is a big worry when storing sensitive data for a business on the cloud. Although cloud service providers use sophisticated security procedures, there are still security concerns when keeping sensitive data on distant computers that are wholly owned and controlled by a third party.
The cloud provider and the user share responsibilities for IT security when a company chooses a cloud computing strategy. As a result, each stakeholder is accountable for the resources, operations, and procedures within their control.
5. Data loss or theft: Storing important data in virtual data centers might expose you to a number of dangers that could result in data loss, including credential theft, information theft, cloud misconfiguration, and security breaches.
Additionally, cloud service providers like Microsoft and Google use a shared responsibility model in which the customer is still in charge of the application’s data, administration, and user management while the vendor is responsible for the availability of the application and everything that goes with it.
Three-Step Guide for SaaS Data Protection
Transferring sensitive information from on-premises programs to cloud-based ones like Salesforce, Office 365, or G Suite? Congratulations!
Your SaaS provider is offering a solid foundation to maintain the availability of your data, so it is in excellent hands. However, you must play a role in keeping it secure.
To safeguard your data in SaaS programs against anything from accidental deletion to hacking, follow this 3-step strategy.
1. Make Access Simple – Yet Secure
Use these identity and access management best practices to ensure that data reaches the appropriate individuals and stays out of the wrong hands.
Simplify data access: Use repeated onboarding and offboarding procedures, and maintain data in a format that can be restored after offboarding.
Regulating data access: Implement multi-factor authentication and strict password rules while using the security features of your SaaS platform.
2. Protect Data from Loss
By adhering to recommended practices for data security, prevent data loss.
Understand the risks: To better comprehend the data you are storing and exchanging (through APIs) in SaaS applications, use data categorization tools.
Reduce data exposure: Create data security regulations that reduce risk by regulating the kinds of private information stored on SaaS systems.
Be on your guard: Implement preventative and real-time policy enforcement utilizing solutions from SaaS platforms and other third parties.
3. Use the proper backup to safeguard data
Pick a backup program that not only lets you save your data, but also lets you retrieve it quickly, simply, and successfully. Look for a solution that has these features.
Scalability at the enterprise level: A solution that is solidly scalable will be advantageous to both big businesses and smaller companies.
Automated and on-demand backups are both necessary, but you should also have the flexibility to back up data whenever you choose. Daily “set it and forget it” procedures are essential.
Point-in-time restorations that are quick and simple are required by administrators, who also need the flexibility to provide users access to that same functionality.
Multiple levels of operational and physical security are necessary to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and safety of your data.
Suggestions for selecting a cloud computing model
With the best choice of cloud service provider and the proper cloud computing service model they bring to the table, business results may be hastened. It might be difficult to choose the finest cloud computing service models.
The decision would be based on the needs of the organization and a thorough examination of the features, costs, security, and reputation that the cloud service provider brings with it.
The most well-known companies in the sector provide extensively utilized and well-known cloud computing service models. When selecting the ideal cloud computing service model, the following elements must be carefully considered.
These are the basic elements that would be taken into account when your firm was making a decision about the cloud service providers it would choose.
Business Profile
To begin with, choosing the finest cloud provider and appropriate cloud computing service type is greatly influenced by the company’s profile.
The business must be well-known, have a solid track record, be steady, and have no legal or data-related problems with the cloud provider.
Many companies provide cloud services, but some of the most well-known ones include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure (MS-Azure). These cloud service companies presently hold the majority of the market.
IBM Cloud, Dell EMC, Salesforce Cloud, Oracle Cloud, and many more are other participants in the cloud industry. AWS dominates this market despite the fact that each cloud provider has advantages and disadvantages of its own.
Costs
Costs are a significant consideration even if they are not the only one when choosing a cloud service provider. The cost component, as described below, takes into account the following elements:
- Pay as you go suggests that there is no upfront payment and that price is directly according to consumption.
- Reserved – instances that will be held for 1 or 3 years for a one-time fee dependent on use
- Discounts—These are volume discounts provided by the cloud service provider depending on the number of services used.
As the market leader, AWS mostly uses the cost model mentioned above, while other significant competitors use benchmarks that are somewhat comparable.
Billing for instances on the Google cloud platform is done by the second. Depending on the exact product offering, Microsoft Azure bills the clients on-demand by the hour, gigabyte, or millions of executions.
Making an appropriate decision about a cloud provider and cloud service platform necessitates cost comparisons.
Technology and Assistance
The alignment of your company’s architecture with that of the cloud provider should be taken into consideration when choosing a cloud computing service model.
For instance, choosing Microsoft Azure as a service provider over other market rivals might make more commercial sense if your company has a significant investment in the Microsoft ecosystem.
A firm must consider whether the cloud provider gives help for migration and other assistance when selecting a cloud provider and the cloud computing service model.
It must also consider the number and kind of modifications that would be required along the whole process.
Data Governance and Security
The first emphasis must be security. To make sure that the cloud service model provided by the cloud provider complies with standards like the ISO 27000 series and that their certifications are legitimate, checks must be made.
Every business must thoroughly investigate any legislative obligations that can be relevant to data governance and security when it comes to security.
The security check must also confirm that the cloud provider’s security measures complement the company’s current security and policies and are risk-based.
Performance and dependability
Verify the procedures, roles and responsibilities, resources, and disaster recovery plans of the cloud provider. The reliability and performance matrix of a cloud service model offered by the cloud provider may be assessed in a number of different ways.
Validating the cloud provider’s performance vs their SLA for the last 6–12 months is the first and most crucial way to assess performance.
Although it is customary to provide this information, if it is not, the service provider may be directly contacted, and performance information must be verified. Although downtimes are unavoidable, what counts is how the cloud
provider handles them and how well your cloud service provider handles them. The cloud service provider must be able to demonstrate to you how they have successfully managed both scheduled and unforeseen downtime in the past.
Such performance statistics may increase your trust in choosing the finest cloud provider, allowing you to choose the best cloud computing service model.
Integration, Service Dependencies, and Partnership
The selection criteria for cloud vendors must take into account the whole ecosystem, not just a particular product, of the cloud provider.
It’s important to be aware of the vendor’s relationship network in advance and to make sure that the partnerships are solid and reputable. The following variables must be taken into account while choosing a partnership and service dependencies:
- Service Provision
- Business lingo
- Data Security
- Legal Defenses
It is crucial to consider service levels and delivery in order to be certain and have a confident opinion on their accessibility, responsiveness, capacity, and assistance.
When choosing a cloud provider and the optimal cloud computing service model, cloud service level agreements are a key factor.
A business may successfully develop a solid foundation if they choose the service provider by taking into consideration these crucial factors.
The firm will be able to make an educated selection if it does detailed work and in-depth study of the organization’s needs before moving forward with the cloud service provider.
The firm will subsequently be able to put its faith in the cloud service provider that is providing the cloud platform with regard to its data and applications.
The cloud is the workplace and business of the future. Currently, 81 percent of businesses have a multi-cloud strategy, and by 2023, it is predicted that $500 billion would be spent on cloud infrastructure.
I hope you have got a very clear idea about this trending technology. Now, share your opinion and experience about cloud computing the comment box bellow.
Recommended for you:
Best 100 plus online business ideas for you
Branches of graphics design and what to learn?
How to become successful in artificial intelligence?



Simply wanna comment that you have a very nice internet site, I love the design it really stands out.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive learn something like this before. So nice to seek out any person with some authentic ideas on this subject. realy thank you for beginning this up. this website is something that’s needed on the web, somebody with a little bit originality. useful job for bringing one thing new to the web!