SSL stands for Secured Sockets Layer. SSL certificate means is one of the most important things when you want to make a website of your own.
Although there are many types of SSL certificate we will discuss here about classifications of SSL certificates as well as how to get them.
What will happen when they are expired. Let’s begin with what is SSL Certificate. Then we will go to the types of SSL Certificate.
What is SSL Certificate?
An SSL certificate is a kind of internet security certificate that creates an encrypted connection and verifies the identity and authenticity of a website.
The data security technology known as SSL, or Secure Sockets Layer, establishes an encrypted connection between your browser and the website server.
Particularly for businesses and organizations that make online transactions involving customers’ data and financial information, the degree of security provided by SSL certificates has become standard practice on reliable websites.
The underlying SSL meaning hasn’t changed despite several revisions of SSL certificates over the years, each with some inherent security issues.
TLS, or Transport Layer Security, is the most recent version of SSL and has essentially taken the role of older SSL protocols. The two phrases are often used interchangeably, even if this has slightly complicated any SSL explanation.
By allowing a browser to rapidly authenticate a website’s authenticity and create a secure, encrypted connection, SSL certificates, together with anti-tracks and other cybersecurity technologies, help safeguard user data and privacy.
Read more about Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Why is SSL Certificate so important?
You need an SSL to connect securely with a website and safeguard data transfers since we often exchange critical information online.
You are protected against fraudulent or compromised websites and hackers by SSL certificates, which authenticate a website’s identity and credentials and encrypt your connection to the website.

SSL certificates assist to safeguard your data from being stolen and auctioned off by encrypting your connection during exchanges across websites. For website security, SSL is essential, especially when processing payments online.
For cybercriminals, selling financial data, passwords, and other personal information to data brokers or dubious characters on the dark web is lucrative.
Take quick action to avoid fraud in the case that data is stolen, and notify the appropriate authorities of the cybercrime.
It’s a good idea to do a dark web scan to make sure your data hasn’t been exposed in a data breach even if you don’t believe you’ve been hacked.
You may like 15 most important cyber security tips for your business.
How do SSL certificates work?
While confirming a website’s authenticity and identity, SSL certificates encrypt the communication between a website and your browser.
Companies employ SSL protocols and other data encryption methods to encrypt online data so that unauthorized third parties cannot decode it.
How SSL certificates work may be explained by understanding the SSL handshake. Before establishing a connection, a website and your browser must first authenticate one another via the SSL handshake.
The SSL handshake goes as follows:
- Your browser asks the web server for confirmation when attempting to connect to a site that has SSL certification.
- A copy of the server’s SSL is sent.
- Your browser determines whether to trust the website after reviewing the SSL certificate. In such a case, your browser tells the web server about this trust.
- To initiate an SSL-encrypted connection, the web server digitally signs and transmits an acknowledgment.
- Then, encrypted data may be freely shared between your browser and the web server.
The security of SSL connections is guaranteed by the intricate SSL handshake, which takes place extremely instantly and has no effect on your surfing experience.
Why is an SSL certificate need for websites?
To authenticate themselves, create secure connections, and develop user trust, websites need SSL certificates.
SSL indicates that the website is authentic and that all transactions are encrypted and secure, which is crucial for companies. Because of this, website verification uses SSL certificates as a norm.
But is an SSL required with the variety of cybersecurity technologies available? One of the main advantages of a VPN is an encrypted connection, similar to SSL protocols.
Additionally, the top browsers for privacy and security may aid in preventing cookie-based tracking and identity theft.
What does an SSL certificate accomplish for you, then?
Having peace of mind as a person is provided by websites with SSL certificates. You may take precautions to guard against online dangers, but you also want the websites you visit to look out for you.
SSL guards against prying eyes and hazardous hackers by encrypting your name, address, passwords, bank information, and other data.
Types of SSL certificate
There are several sorts of SSL certificates, each with a distinct degree of security. A more sophisticated SSL certificate protocol is seen as being more secure than a simpler SSL certificate, and this is true for both types of websites. The cost of a more reliable SSL infrastructure, however, is more.
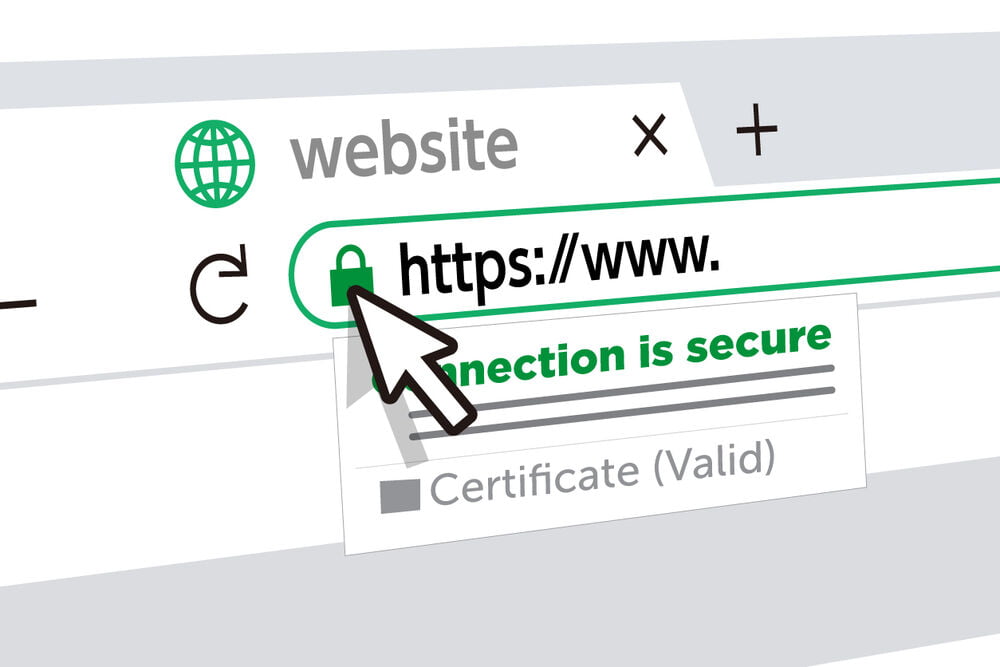
The applicable Certificate Authority (CA), which subsequently provides the SSL certificate, must be paid by website owners to get a certain level of SSL certification.
There are many types of SSL Certificates which are given bellow;
Extended Validation certificates (EV SSL)
Highly respected websites that gather data and process payments online utilize EV SSL, the costliest and most secure SSL certification.
To distinguish legitimate websites from fraudulent ones, EV SSL certificates show a padlock, HTTPS, the company name, and the country of origin in the address bar.
A website must demonstrate that it is entitled to possess the domain to acquire an EV SSL. Visitors are reassured that the data being collected for transactions and online payments are lawful.
Organization Validated certificates (OV SSL)
User data during transactions is encrypted as part of OV SSL’s primary function. A medium degree of encryption is provided by OV SSL in comparison to EV SSL. Additionally, it confirms the validity of your company and domain.
A green padlock with the company’s name is shown by OV SSL in the address bar of the browser. The CA confirms the domain’s ownership and its legal status before issuing an OV SSL.
Domain Validated certificates (DV SSL)
Sites without data transfers or payments, such as informative websites, often display the DV SSL certification. DV SSL is less encrypted and secure than the other certificates on the above list since it needs minimum validation.
Website visitors won’t know who is getting their encrypted data using DV SSL since the CA won’t check identification information. In the browser’s address bar, DV SSL only shows a green padlock.
Wildcard SSL certificates
In addition to an infinite number of subdomains, wildcard SSL certificates may be used for your primary domain. As part of the common name, which applies to the primary domain and all sub-domains, wildcard SSL certificates are identified by an asterisk (*).
For website owners who can’t afford to buy several SSL certificates, wildcard SSL certificates are a more affordable option.
The Wildcard SSL certificate, for instance, may be applied to your primary website and then used for your site’s email and blog subdomains.
Unified Communications Certificates (UCC)
These certificates, sometimes referred to as Multi-Domain SSL certificates (MDC), may be used to show a padlock in the browser address bar for up to 100 main domains and subdomains. Upgrades to EV SSL certificates are available for UCCs and MDCs.
The best method to get an SSL certificate
Directly from a Certificate Authority (CA), SSL certificates may be purchased. Millions of SSL certificates are issued annually by certificate authorities, also known as certification authorities.
They are essential to the functioning of the internet and to the ability of online users to engage in interactions that are open and trustworthy.
Depending on the amount of security you need, an SSL might cost anywhere from nothing to hundreds of dollars.
You may search for Certificate Issuers that provide SSLs at the required level after you have decided on the sort of certificate you need.
These procedures must be taken to get your SSL:
- Set up your server and check that your WHOIS record is current and matches the information you are providing to the Certificate Authority to get ready (it needs to show the correct company name and address, etc.)
- On your server, create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). Your hosting provider can help you with this.
- Sending this to the Certificate Authority for verification of your domain name and business information
- Once the procedure is finished, you must install the certificate they provide you.
After obtaining the certificate, you must configure it on your web host’s servers or, if you are hosting the website yourself, on your servers.
What kind of certificate you acquire and whatever certificate provider you buy it from will determine how fast you get it. It takes a variable amount of time to complete each stage of validation.
In contrast to Extended Validation, which may take up to a week, a basic Domain Validation SSL certificate can be given in only a few minutes.
What happens if the SSL certificate has expired?
SSL certificates do eventually expire; this is true. SSL certificates should have a lifetime of no more than 27 months, according to the Certificate Authority/Browser Forum, which acts as the de facto governing authority for the SSL business.
This effectively implies two years, plus you may carry over up to three months if you renew your SSL certificate while it still has time on it.
SSL certificates expire because, like with any kind of authentication, data must be regularly revalidated to ensure that it is still correct.
Companies and websites are purchased and sold on the internet, which causes things to change. The details of SSL’s also change when they are transferred.

To guarantee that the data used to authenticate servers and organizations is as current and accurate as possible, the expiration period was created.
SSL certificates could formerly be granted for up to five years, however, this was later decreased to three years, and most recently to two years plus a possible additional three months.
Despite the Certificate Authority Browser Forum’s rejection of this idea, Google, Apple, and Mozilla declared in 2020 that they will mandate one-year SSL certificates.
This started in September 2020. The validity period may probably become even shorter in the future.
A website becomes inaccessible when its SSL certificate expires. Within milliseconds of a user’s browser accessing a website, it verifies the authenticity of the SSL as part of the SSL handshake.
Visitors will get a warning that says “This website is not secure” if the SSL has expired. possible danger up ahead “.
Users do have the choice to continue, but it is not recommended given the cybersecurity dangers, which may include the presence of malware.
As people quickly leave the homepage and visit other websites, this will have a substantial influence on bounce rates for website owners.
It may be difficult for bigger enterprises to keep track of when SSL expire. Enterprise-level firms with several websites and networks that may do business globally would likely have many more certificates than smaller and medium-sized businesses (SMEs), which may only have one or a few.
At this level, letting an SSL expire is more often a consequence of oversight than stupidity. Using a certificate management tool is the most effective approach for bigger enterprises to keep track of when their SSL certificates expire.
You may locate a variety of items on the market by doing an internet search. With the help of these, businesses may see and manage all of their digital certificates.
It is crucial to periodically check in if you utilize one of these platforms so you can be informed of when renewals are due.
If a certificate expires, it becomes invalid and your website will no longer be able to conduct secure transactions. Before your SSL certificate expires, the Certification Authority (CA) will remind you to renew it.
You will get expiry alerts at predetermined intervals, often beginning at least 90 days in advance, from the Certificate Authority or SSL provider you used to acquire your SSL certificates.
Instead of sending these reminders to a single person, who could have left the firm or moved to a different position by the time the reminder is delivered, try to send them to an email distribution list.
To make sure the appropriate individuals get the reminders at the appropriate time, consider which corporate stakeholders are on this distribution list.
You can visit wikipedia to read more about SSL if want.
Recommended for you:
Best 11 ways to get more traffic to your website?
How to find ideal hosting for your website?
8 best techniques of how to make a user friendly website
How to increase sign ups for membership site?
10 Best way of how to make money blogging
10 best investment ideas to increase money
Top 30 latest technologies of 2022 | Best trending technologies